When it comes to the Internet, you’ve probably heard about IPv4 and IPv6. But what do these terms mean, and why are they important? In this post, we’re going to break down the differences between IPv4 and IPv6 in a way that’s easy to understand. So, let’s dive into https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion and learn why these protocols matter for your online experience.
IPv4 has been around for a long time, but with more and more devices connecting to the internet, we’re running out of IPv4 addresses. That’s where IPv6 comes in. It’s the newer version that solves the problem of limited addresses and offers other improvements. By the end of this post, you’ll know why IPv6 is the future and how it will impact your daily internet use.
What Is https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion? Understanding Internet Protocol Basics
The Internet Protocol (IP) is a set of rules that helps devices communicate over the internet. When you send or receive data, like a message or a picture, it travels across networks using IP. IPv4 and IPv6 are two versions of these protocols, and they play a key role in how data moves from one place to another online. Without IP, your devices wouldn’t be able to connect to websites, apps, or even other devices.
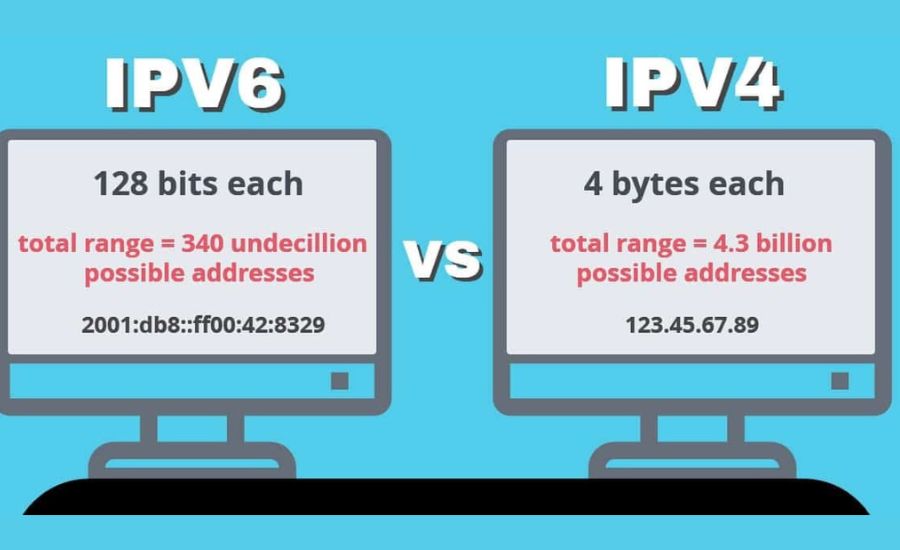
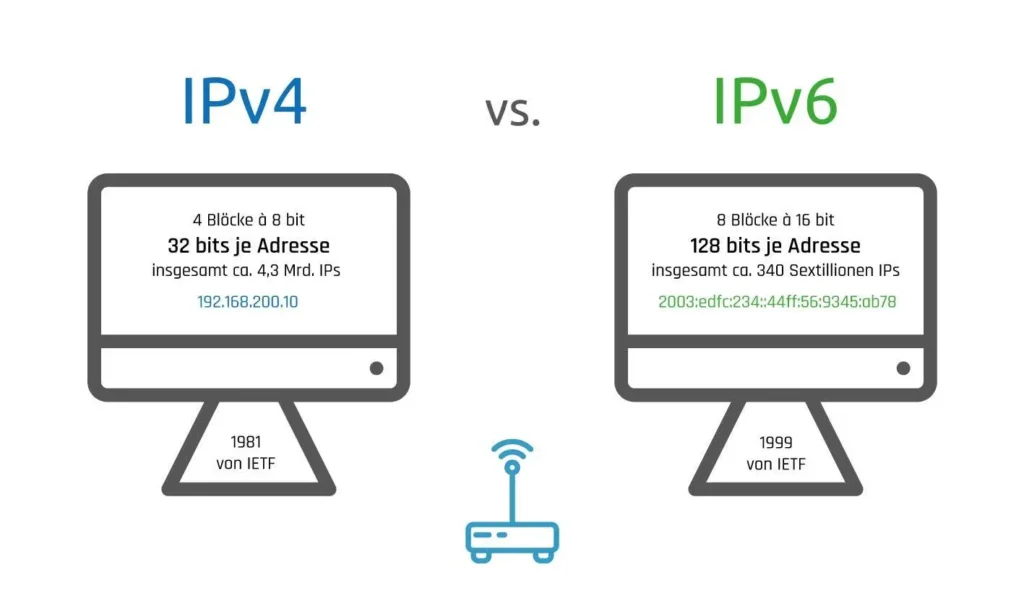
IPv4, the older version, has been in use since the early 1980s. It uses a 32-bit address system, which is enough to provide around 4.3 billion unique addresses. However, with the explosion of the internet and the increase in connected devices, we are running out of IPv4 addresses. This is where IPv6 comes into play. IPv6 is the newer version of the Internet Protocol, using a 128-bit address system, which offers a nearly infinite number of unique addresses.
IPv6 was developed to solve the issue of address exhaustion. It also includes other improvements like better security features and more efficient routing. As more devices connect to the internet, understanding the basics of IPv4 and IPv6 helps us see why IPv6 is becoming increasingly important.
The Evolution of Internet Protocols: From IPv4 to IPv6
IPv4, or Internet Protocol version 4, has been the backbone of internet communication for decades. It has served us well, but as more people and devices started using the internet, we quickly realized that we were running out of IP addresses. IPv4’s 32-bit addressing system just wasn’t enough to support the growing demand for unique IP addresses.
IPv6, or Internet Protocol version 6, was introduced to address this problem. Unlike IPv4, which offers 4.3 billion addresses, IPv6 provides a staggering 340 undecillion addresses. This massive increase in available addresses ensures that we won’t run out of IP addresses anytime soon, even as more devices join the internet.
The transition from IPv4 to IPv6 has been gradual because it’s a significant change. Many systems and networks still rely on IPv4, but the shift to IPv6 is essential for the future of the internet. With IPv6, we not only solve the address exhaustion problem but also gain other benefits like improved security and efficiency in data routing.
Comparing IPv4 and IPv6: Key Differences You Should Know
The most noticeable difference between IPv4 and IPv6 is their address format. IPv4 addresses are written as four numbers separated by periods, like 192.168.1.1. On the other hand, IPv6 addresses are much longer, written in hexadecimal and separated by colons, such as 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334. This difference in format is due to the size of the address space each protocol supports.
IPv4 uses a 32-bit address system, which limits the number of unique IP addresses to about 4.3 billion. This seemed like plenty when the protocol was first created, but it’s no longer enough. IPv6, however, uses a 128-bit address system, providing a nearly unlimited number of addresses. This vast address space is essential for supporting the growing number of internet-connected devices.
Beyond just the address format, IPv6 also brings other technical improvements. It simplifies packet processing, supports better security features like IPsec, and allows for more efficient routing. These enhancements make IPv6 a more robust and future-proof protocol, ensuring that it can handle the demands of the modern internet.
Why https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion Matters: The Need for More IP Addresses
As the internet continues to grow, so does the number of devices that need IP addresses. Every smartphone, computer, smart home device, and even many vehicles require a unique IP address to connect to the internet. With IPv4, the limited number of available addresses has become a significant challenge, leading to the need for a more extensive system.
IPv6 was created to solve this issue by offering an enormous number of unique IP addresses. This is crucial because, as more devices connect to the internet, the demand for IP addresses will only increase. IPv6 ensures that there will be enough addresses to go around, even as we add billions of new devices to the internet.
This need for more IP addresses is also important for future technologies. The Internet of Things (IoT), for example, relies on billions of devices being connected and communicating with each other. IPv6 makes it possible to support this vast network of devices, ensuring that the internet can continue to expand and evolve.
Understanding IPv4 Limitations and How IPv6 Solves Them
IPv4 has served the internet well for many years, but it has some limitations that are becoming more apparent as the internet grows. The most significant limitation is the number of available IP addresses. With only 4.3 billion possible addresses, IPv4 cannot support the increasing number of internet-connected devices.
Another limitation of IPv4 is its reliance on Network Address Translation (NAT). NAT allows multiple devices on a local network to share a single public IP address, but it also adds complexity and can slow down network performance. IPv4 also lacks built-in security features, relying on external solutions like IPsec to provide encryption and data integrity.
IPv6 addresses these limitations with a much larger address space, eliminating the need for NAT and simplifying network configurations. It also includes IPsec as a standard feature, providing better security out of the box. These improvements make IPv6 a more scalable, secure, and efficient protocol, better suited to meet the needs of the modern internet.
IPv6 Security Benefits: Enhanced Protection for the Modern Web
One of the standout features of IPv6 is its enhanced security, making it a better choice for today’s internet. Unlike IPv4, IPv6 has built-in support for IPsec (Internet Protocol Security), which provides end-to-end encryption and ensures that data being sent over the internet is protected. IPsec makes it harder for attackers to intercept or tamper with data, offering a higher level of security for online communications.
The inclusion of IPsec in IPv6 means that security is no longer an afterthought or an optional extra. It’s baked into the protocol, ensuring that all data traveling through IPv6 networks can be encrypted and authenticated. This is particularly important as more sensitive information is shared online, from financial transactions to personal data.
Furthermore, IPv6’s larger address space also plays a role in improving security. It makes scanning and attacking networks more difficult for hackers. With the increasing number of cyber threats, these security enhancements in IPv6 are crucial for protecting users and businesses alike. As the internet evolves, the robust security features of IPv6 will become even more essential.
The Future of Internet Protocols: Will IPv6 Replace IPv4 Completely?
IPv4 and IPv6 are currently coexisting, but many experts believe that IPv6 will eventually replace IPv4 completely. The transition has been slow, largely because so many systems and networks still rely on IPv4. However, as the number of connected devices continues to grow, the limitations of IPv4 become more apparent, driving the need for a complete switch to IPv6.
While IPv4 is still in use today, IPv6 adoption is steadily increasing. Some regions and industries are moving faster than others, with many new devices and networks being built to support IPv6 from the start. However, the full transition to IPv6 will take time, as it requires significant changes to existing infrastructure and systems.
In the future, we can expect IPv6 to become the dominant protocol, especially as older IPv4 systems are phased out. For now, dual-stack networks that support both IPv4 and IPv6 are common, allowing a gradual transition. Eventually, as the benefits of IPv6 become more widely recognized and adopted, IPv4 will likely be retired, paving the way for a more secure and scalable internet.
Don’t Miss Out: Farsiplex
Real-World Applications: Where https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion Makes a Difference

IPv6 is already making a difference in several key areas, particularly in the Internet of Things (IoT) and mobile networks. With the vast number of devices that need to connect to the internet, from smart home gadgets to industrial sensors, IPv6’s large address space is essential. It allows each device to have its unique IP address, which simplifies communication and improves security.
In mobile networks, IPv6 is becoming increasingly important. As more people rely on smartphones and tablets, the demand for IP addresses has skyrocketed. Mobile carriers are adopting IPv6 to meet this demand and to provide better service. IPv6 also enables more efficient data routing, which can lead to faster and more reliable mobile internet connections.
Beyond IoT and mobile, IPv6 is being used in cloud computing and large-scale data centers, where the need for scalability and security is paramount. These real-world applications highlight how https://acortaz.eu/ipv4-e-ipv6-comparacion is playing a crucial role in the continued growth and evolution of the internet, ensuring it can support future innovations.
How IPv6 Improves Internet Performance and User Experience
IPv6 not only provides more addresses but also improves overall internet performance. One way it does this is by simplifying packet processing. With a more streamlined header compared to IPv4, IPv6 allows routers to handle data more efficiently, which can lead to faster data transmission and lower latency.
Additionally, IPv6 eliminates the need for Network Address Translation (NAT), a technique used in IPv4 to conserve addresses. NAT can introduce delays and complicate the routing process, but with IPv6’s vast address space, each device can have its unique IP address without needing NAT. This direct addressing can improve connectivity, leading to a smoother and faster user experience.
Moreover, IPv6 supports better multicast routing, which is beneficial for services like streaming and online gaming. By improving how data is distributed to multiple destinations simultaneously, IPv6 enhances the performance of these services. As a result, users can enjoy faster speeds, more reliable connections, and a better overall internet experience with IPv6.
The Challenge of Transitioning from IPv4 to IPv6: What You Need to Know
Transitioning from IPv4 to IPv6 is not without its challenges. One of the biggest hurdles is the need to update existing infrastructure. Many networks, devices, and applications were built with IPv4 in mind, and upgrading them to support IPv6 requires time, effort, and investment. This is why many organizations opt for a dual-stack approach, running both IPv4 and IPv6 simultaneously.
Another challenge is ensuring compatibility. Not all devices and services are fully compatible with IPv6 yet, which can create issues during the transition. Tunneling techniques, where IPv6 packets are encapsulated within IPv4 packets, are often used to bridge the gap. However, this can add complexity and impact performance.
Despite these challenges, the transition to IPv6 is essential for the future of the internet. To make the switch smoother, organizations need to plan carefully, invest in training, and gradually upgrade their systems. As more networks move to IPv6, the transition will become easier, helping to ensure that the internet remains scalable, secure, and ready for future growth.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, IPv6 is the future of the internet, offering more addresses, better security, and improved performance compared to IPv4. As more devices connect to the internet, IPv6 will become even more important to keep everything running smoothly. While IPv4 has served us well, it’s clear that IPv6 is the better choice for the modern web.
Switching from IPv4 to IPv6 might take time, but it’s worth the effort. With its many benefits, IPv6 ensures that the internet can grow and evolve to meet our needs now and in the future. So, whether you’re browsing, gaming, or using smart devices, IPv6 is here to make your online experience faster, safer, and more reliable.
Read Next: David-Huynh-Utah